Energy Balancing of Non-residential Buildings (according to German DIN 18599)
With the implementation of the German Energy Saving Ordinance 2007 a complex procedure was established which allows the all-inclusive Balancing of Non-residential Buildings - the German DIN V 18599. In contrast to the standards for Residential Buildings (DIN 4108-6 und DIN 4701-10) it is possilbe to model almost all heating systems. The air-conditioning, ventilation and lighting is implemented as well.
Overview DIN V 18599
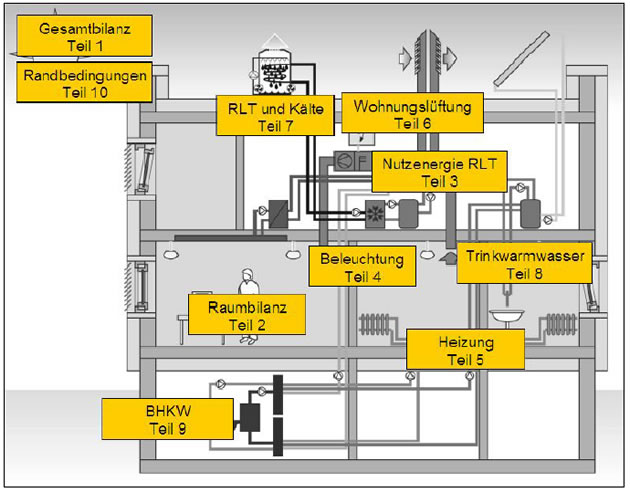
The arround 1000-sided DIN is structured in ten parts:
Calculations according to DIN V 18599
Zoning:
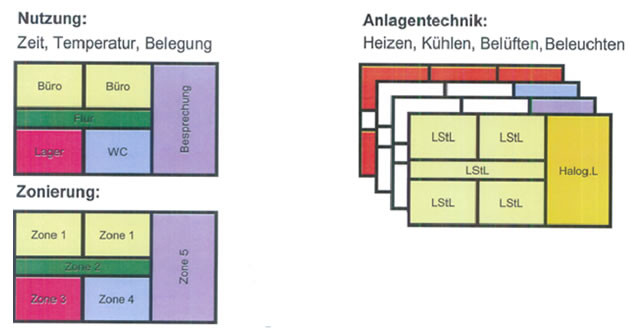
The proof according to DIN V 18599 includes the Zoning of the building into sections suspended to similar usage conditions. There is a range of different profiles for this. If the selected zones are conditioned differently they are subdivided further. Differing ventilation and air-conditioning lead to an additional differentiation.
Coverage Areas:
After finishing the Zoning, Coverage Areas are determined. A Coverage Area pools areas of the building which are supplied with the same technology.
Input of Lateral Surfaces:
The Input of Lateral Surfaces is done for all thermally conditioned areas depending on zones and members. This input reflects the level of insulation of the object.
Roombalance:
The Roombalance is determined taking into account all heat sinks (heat loss due to transmission through exterior members, heat loss due to ventilation) and heat sources (solar entries, aparatuses, people, lighting). The emerging difference is called need of useful energy (winter) or need of useful cold (summer) respectively.
Ventilation system:
The ventilation system is modeled using an exact definition of the type of ventilation, central aparatus, their distribution and transfer. In the simplest case a exhaust air unit, which is installed in an inner bathroom, is sufficient.
Lighting:
Taking the zone alignment and presence of shadow casting objects into account the supply of daylight is determined. Interior zones therfore are frequently not supllied with sufficient daylight and require an increased use of artificial light sources. The selection of the lighting system is done by using details of the type of lamps and motion detectors as well as control systems which are sensitive to daylight. The unintended thermal conditioning by the lighting is determined and treated as a heat source of the appropriate zone.
Heating system / warm water system:
The heating system is defined by the energy source, a detailed depiction of the selected system (district heating, heat pumps etc.), the distribution, the transfer (surface heating, radiator etc.) as well as the regulation and storage. If it is a very complex system the determination of the system type is done with the aid of specialist MEP engineers.
Interconnection:
An identical model of the structure is created by the interconnection of the system type, the zones and structural parameters.
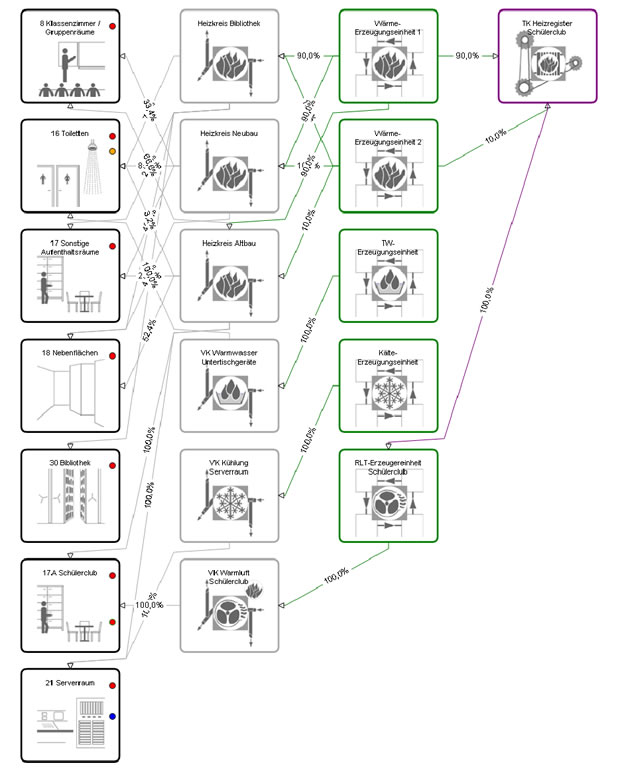
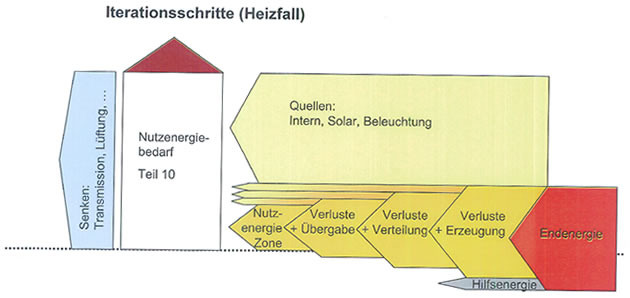
Balancing:
The need of useful heat or cold is first determined approximately seperate for days of work and days without work. The prelimitary amount of heat is apportioned among the supply systems and after that the loss due to storage, distribution and transfer is calculated. During the generation and transport of heat, zones can be conditioned "unintended" so that the final balance of the structure is obtained by an iterative repitition of the previous steps.